A new newsletter a new test device. Due to the very positive effect our Triscan Test Center has on our customer service and internal quality assurance service, we continue to invest in expanding it. Our newly built ABS tester is the latest addition. Here we describe how this works and why it is so valuable.
In order to offer the widest range of ABS sensors on the market, we trade with more than 23 different manufacturers. "We supply around 1,500 different ABS sensors that undergo a 100% functional control in the manufacturing process. Among other things, we use our in-house test equipment in the development phase of new sensors to ensure that they meet the OE specifications. We also use the test equipment to provide properly documented and extensive responses to our customers in case of complaints", says Asger Thybo Geertsen, Triscan Product Team Manager, continuing:" The technology in an ABS sensor is the same as in camshaft and crankshaft position sensors. Our test equipment can therefore also serve the same purpose for these types of sensors".

Two types of ABS sensors
There are basically two types of ABS sensors: The simple type is a passive sensor with built-in solenoid. This type can often be recognized by a visible metal part on the sensor head. Together with a rotating toothed ABS ring, the sensor creates a sine wave when connected to an oscilloscope. This sensor type comes in 2- and 3-wire versions. In the 3-wire version, the third wire is for noise isolation only.
After an error code points to the ABS system, many mechanics are looking for the error only by measuring the resistance of the sensor with a multimeter. However, a complete test of the ABS sensor, in reality, also requires the measurement of the magnetic coil's ability to produce a magnetic field/induction which is not possible with a conventional multimeter. However, there are special multimeters that can measure the induction, which is measured in millihenry (mH). Troubleshooting based solely on resistance measurement may result in the mechanic falsely believing that other parts of the ABS system, such as an ABS ring or ABS module, are defective.
The other type of ABS sensors uses Hall effect chips and is available in two versions - active and inductive sensors. The active uses a magnetic ABS ring and the inductive uses a traditional toothed ABS ring. Both types provide a square wave signal on an oscilloscope and none of these types can be diagnosed with a multimeter. With an oscilloscope, however, it is possible to check the reading of speed and teeth. Not even a magnetic card reader can detect whether a tooth on the ABS ring is defective or missing.
DID YOU KNOW:
• All OE sensor manufacturers use Hall effect chips manufactured by either Allegro, Infinion, Melexis or Honeywell?
• We use original Hall effect chips in our sensors? The make and article number of the chip in the original sensor is revealed by x-raying the sensor.
Features and Disadvantages of the Passive Sensor:
Passive sensors are no longer widely used because they produce an irregular signal in the event of high temperature fluctuations. Modern auxiliary systems such as ESP, TPMS require a more stable signal than the passive sensor can provide. For passive sensors, the critical values are VPP (Voltage Peak to Peak), resistance and induction (Rising Edge and Falling Edge).
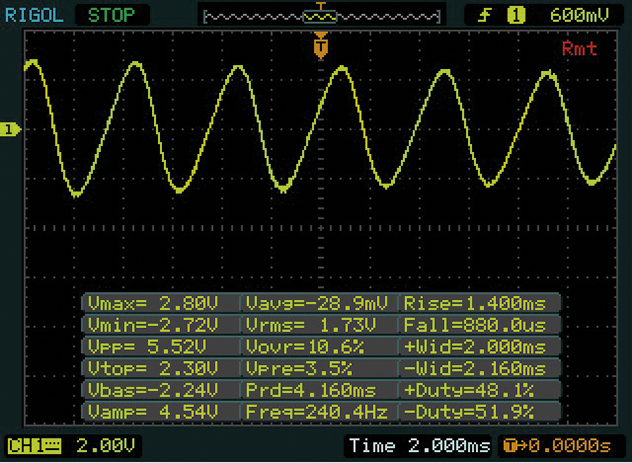
Here you see a passive ABS sensor that works with a passive coil. This provides a wavy signal
Features and Benefits of the Active Sensor:
The active sensor, which in most cases uses a Hall effect chip, provides a more stable signal at fluctuating temperatures. It is therefore much better suited for use with ESP, TPMS systems. The critical values for this are: pulse width, Vmax, Vmin and frequency.

Here you can see the square wave signal from an active or inductive ABS sensor (Hall effect chip). Active sensors work with magnetic ABS rings and inductive sensors with toothed ABS rings
Vehicles with Parking Assist use special Hall effect chips that can count the teeth of the ABS ring and determine the direction of rotation of the wheel. This information allows the vehicle to accurately calculate how far it is moving and is also used to automatically park the car with the help of information from the parking sensor, amongst others.

Here you can see the square wave signal from an ABS sensor with a Hall effect chip capable of counting teeth and detecting the direction of rotation of the wheel
How do we test ABS sensors?
To test whether an ABS sensor is working properly, we always compare it to an original sensor. Two of the most important parameters are voltage level and duty cycle. The voltage level determines whether the quality of the signal is strong enough and the duty cycle indicates whether the sensor measures the rotation correctly. The results of these measurements are included in the reports our customers receive in cases of complaints.








